AIM Act HFC Phasedown Schedule: Final Ruling
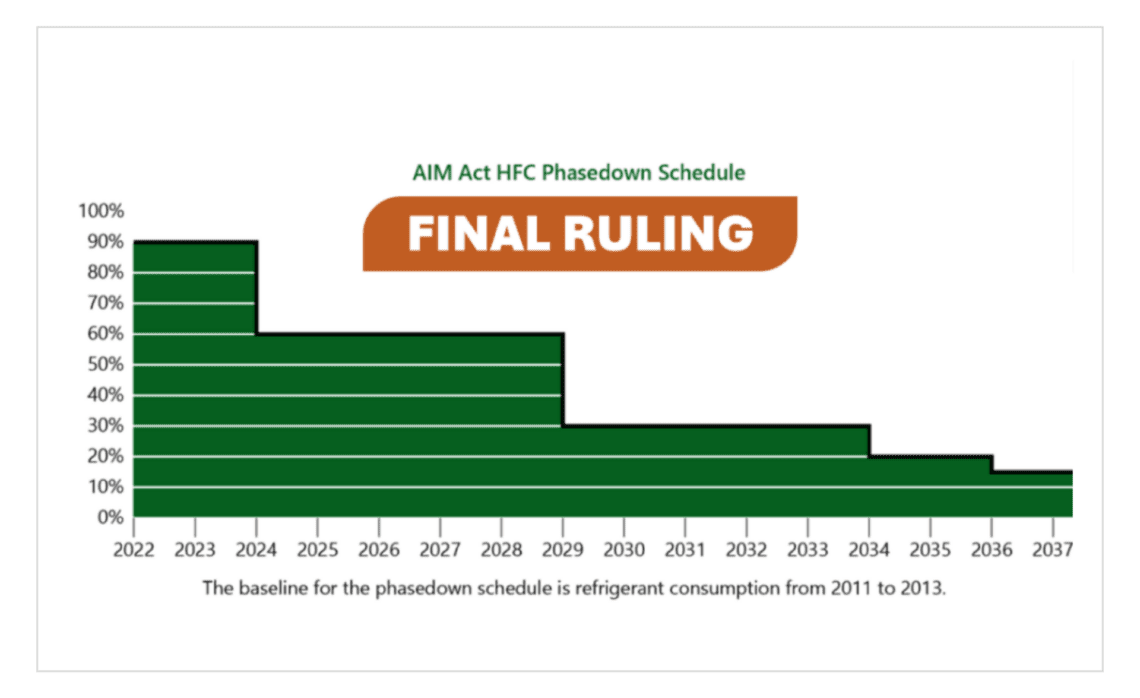
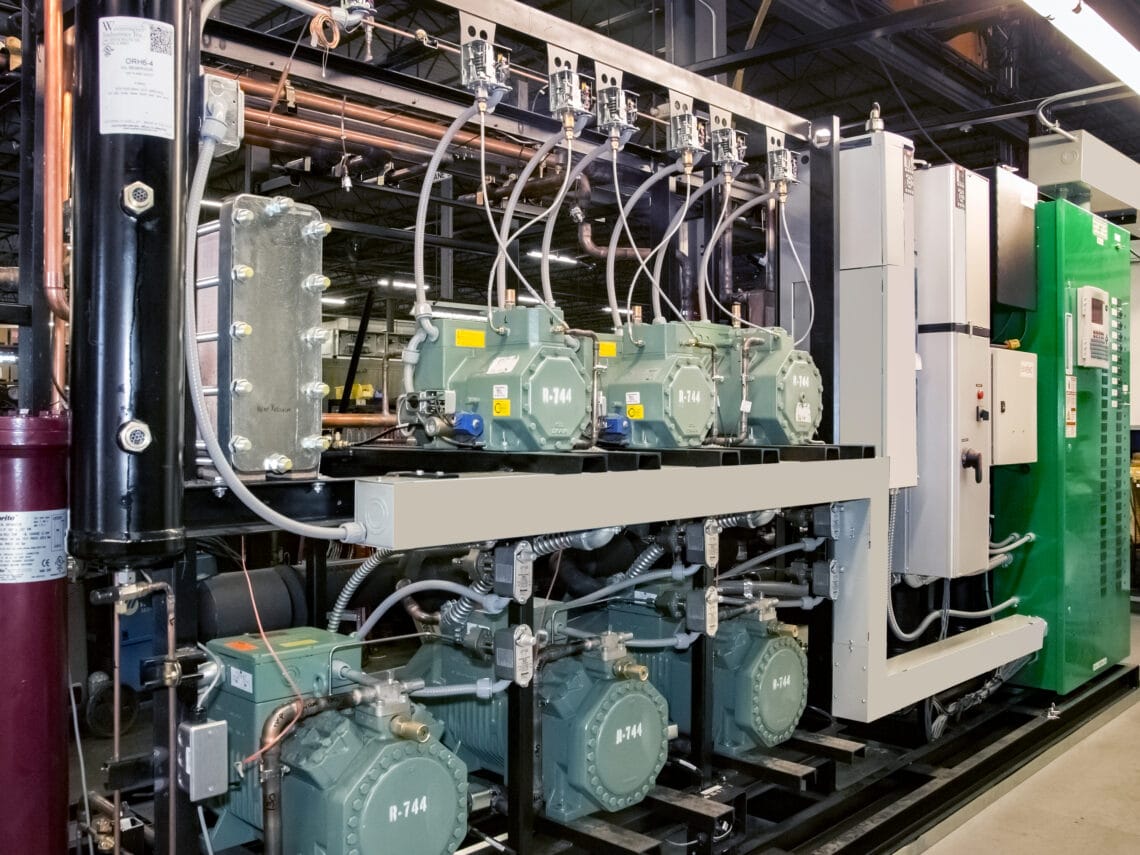
The AIM Act directs the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to oversee the phasedown of HFC refrigerant production and consumption in an effort to transition to alternative refrigerants. The AIM Act includes a phasedown schedule that began in 2022 and continues to 2036.
The new rule prohibits the manufacture and import of self-contained products that use hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). The rule also prohibits the sale, distribution, and export of products three years after the manufacture and import restriction. Finally, it prohibits the installation of new refrigeration air conditioning and heat pump (RACHP) systems that contain HFCs. The compliance dates of these new rules vary based on sector and subsector.
The Role of Refrigerants
Every refrigeration system requires four major components to operate:
- The evaporator to absorb heat
- The compressor to move heat
- The condenser to release heat
- The expansion valve to return to the evaporator and start again
Flowing through these components is refrigerant, the other crucial part of refrigeration systems.
- Refrigerant is what absorbs the heat and releases the heat
- Refrigerant is what is compressed and expanded
- Refrigerant is what gets the job done
Types of Refrigerants
R404A
R404A is a widely used hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerant known for its excellent cooling capabilities across a wide temperature range. It has been a popular choice for commercial refrigeration applications, including supermarket freezers, walk-in coolers, and cold storage warehouses.
R134a
An HFC refrigerant, R134a, finds its place in medium-temperature applications such as beverage coolers, refrigerated display cases, and ice machines in commercial settings.
R407A/R407F
These HFC refrigerants are environmentally friendly alternatives to R404A, offering similar performance in low and medium-temperature commercial refrigeration systems.
R410A
R410A is an energy efficient HFC refrigerant primarily used in commercial air conditioning systems, ensuring optimal cooling while complying with environmental regulations.
R744 (Carbon Dioxide)
Known as carbon dioxide, R744 serves as a natural refrigerant with low global warming potential (GWP). It is gaining popularity in trans critical CO2 refrigeration systems for supermarkets and various other commercial applications.
R290 (Propane)
R290, a hydrocarbon refrigerant, is known for its energy efficiency and minimal environmental impact. It is utilized in plug-in refrigerators, commercial freezers, and vending machines, offering sustainable cooling solutions.
R717 (Ammonia)
Ammonia, or R717, is a natural refrigerant used in large-scale industrial refrigeration systems, cold storage warehouses, and food processing facilities. Its excellent heat transfer properties and energy efficiency make it a reliable choice.
Environmental Impact
Future Trends in Refrigerants






